Spring Boot + Spring Security + Hibernate Configuration Example
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure Spring Security Hibernate and Spring Boot. We secure a simple stateless web service using basic authentication. We configure Spring Security using Spring Java and/or XML Configuration. Finally, we write some JUnit Integration Tests with spring-test, h2 in-memory database and MockMvc.
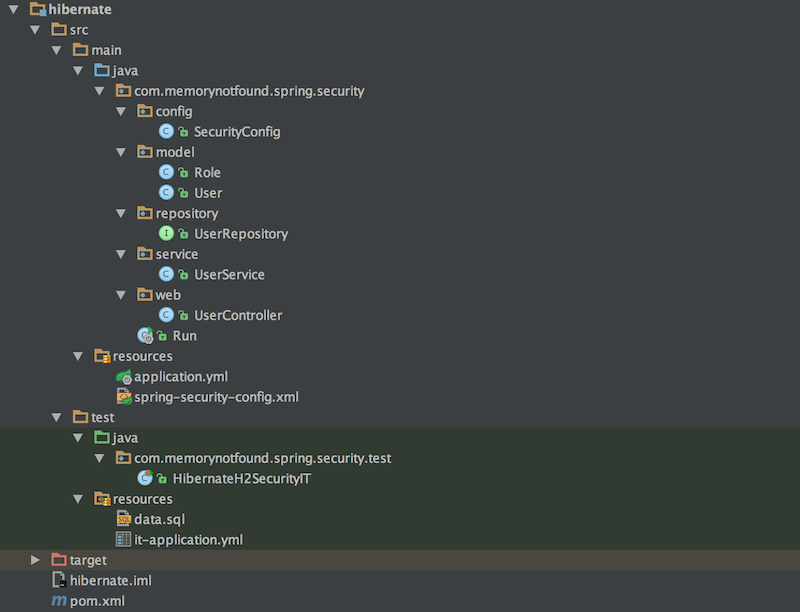
Project Structure
Let’s start by looking at the project structure.
Maven Dependencies
We use Apache Maven to manage our project dependencies. Make sure the following dependencies reside on the class-path.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.memorynotfound.spring.security</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<url>http://memorynotfound.com</url>
<name>Spring Security - ${project.artifactId}</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- testing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Spring Security Configuration
We configure Spring Security using Java Configuration. We configure the DaoAuthenticationProvider by setting the UserDetailsService and the PasswordEncoder. We use the BCryptPasswordEncoder class which uses the BCrypt strong hashing function. Finally, we configure Spring Security to use stateless basic authentication.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.config;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider(){
DaoAuthenticationProvider auth = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
auth.setUserDetailsService(userService);
auth.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
return auth;
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
}
}Here is the equivalent Spring XML Configuration spring-security-config.xml located in the src/main/resources/ folder.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<http create-session="stateless">
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="isAuthenticated()"/>
<http-basic/>
</http>
<mvc:component-scan base-package="com.memorynotfound"/>
<beans:bean id="passwordEncoder"
class="org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder"/>
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="userService">
<password-encoder ref="passwordEncoder"/>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>Spring Security Hibernate Configuration
We configure JPA with Hiberante using the application.yml file located in the src/main/resources/ folder.
Following properties are configured using the DataSourceProperties class.
spring.datasource.url– specifies the JDBC url of the database.spring.datasource.username– specifies the login user of the database.spring.datasource.password– specifies the login password of the database.
Following properties are configured using the JpaProperties class.
spring.jpa.show-sql– enable logging of SQL statementsspring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto– DDL mode. This is actually a shortcut for the “hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto” property. Default to “create-drop” when using an embedded database, “none” otherwise.spring.jpa.database-platform– Name of the target database to operate on, auto-detected by default. Can be alternatively set using the “Database” enum.spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect– specifies which SQL dialect to use.
# ===============================
# = Hibernate datasource
# ===============================
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_security_hibernate
username: root
password:
# ===============================
# = JPA configurations
# ===============================
jpa:
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
database-platform: MYSQL
properties:
hibernate.dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
# ===============================
# = Logging configurations
# ===============================
logging:
level:
root: WARN
com.memorynotfound: DEBUG
org.springframework.web: INFO
org.springframework.security: INFOHibernate POJO Mappings
We are using hibernate annotations to map fields to database columns. Here is the User class.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Collection;
@Entity
@Table(uniqueConstraints = @UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "email"))
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String password;
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.EAGER, cascade = {CascadeType.MERGE, CascadeType.PERSIST})
@JoinTable(
name = "users_roles",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(
name = "user_id", referencedColumnName = "id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(
name = "role_id", referencedColumnName = "id"))
private Collection<Role> roles;
public User() {
}
public User(String firstName, String lastName, String email, String password, Collection<Role> roles) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.password = password;
this.roles = roles;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Collection<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Collection<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", password='" + "*********" + '\'' +
", roles=" + roles +
'}';
}
}Here we configured the Role class.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
public Role() {
}
public Role(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Role{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}Creating User Repository
Create a user repository to lookup the user by email.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.repository;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByEmail(String email);
}Implementing Spring UserDetailsService
We need to implement the UserDetailsService to lookup a user from the database.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.service;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.Role;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.User;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String email) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findByEmail(email);
if (user == null){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Invalid username or password.");
}
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getEmail(),
user.getPassword(),
mapRolesToAuthorities(user.getRoles()));
}
private Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> mapRolesToAuthorities(Collection<Role> roles){
return roles.stream()
.map(role -> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}Simple Rest Service
This rest service maps to the /users URI.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.web;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.User;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping
public List getUsers(){
return userRepository.findAll();
}
} Spring Boot
We initialize the application with a default user. We use Spring Boot to start our application.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.Role;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.model.User;
import com.memorynotfound.spring.security.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Arrays;
@SpringBootApplication
// uncomment if you want to use Spring XML Configuration
// @ImportResource("classpath:spring-security-config.xml")
public class Run {
@Autowired
private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
User user = new User(
"Memory",
"Not Found",
"[email protected]",
passwordEncoder.encode("password"),
Arrays.asList(
new Role("ROLE_USER"),
new Role("ROLE_ADMIN")));
if (userRepository.findByEmail(user.getEmail()) == null){
userRepository.save(user);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Run.class, args);
}
}Spring Security Integration Testing
To verify our configuration we wrote some basic Integration Tests using spring-test, h2 in-memory database, JUnit and MockMvc.
H2 In Memory Database Configuration
For our integration tests, we are using a H2 in memory database. We can configure it in the it-application.yml file, located in the src/test/resources/ folder. We can activate this profile using @ActiveProfiles annotation and Spring’ll automatically load and configure these configurations.
# ===============================
# = H2 data source
# ===============================
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:spring-security-hibernate-test;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
platform: h2
username: sa
password:
# ===============================
# = JPA configurations
# ===============================
jpa:
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create-drop
naming-strategy: org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
database-platform: H2We can initialize our database using the data.sql file located in the src/test/resources/ folder. This’ll initalize our h2 in memory database with data.
INSERT INTO user (id, first_name, last_name, email, password) VALUES (1, 'Memory', 'Not Found', '[email protected]', '$2a$10$RyY4bXtV3LKkDCutlUTYDOKd2AiJYZGp4Y7MPVdLzWzT1RX.JRZyG');
INSERT INTO role (id, name) VALUES (1, 'ROLE_ADMIN');
INSERT INTO role (id, name) VALUES (2, 'ROLE_MANAGER');
INSERT INTO role (id, name) VALUES (3, 'ROLE_USER');
INSERT INTO users_roles (user_id, role_id) VALUES (1, 1);
INSERT INTO users_roles (user_id, role_id) VALUES (1, 2);
Spring Security Hibernate H2 Integration Testing
Here is the actual Spring Security Hiberante Integration Test. We use the @ActiveProfiles('it') to enable our special h2 in memory database configuration. Next, we write some tests using MockMvc to demonstrate a successful login and also an invalid login attempt using basic authentication.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.security.test.web.servlet.request.SecurityMockMvcRequestPostProcessors.httpBasic;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest
@ActiveProfiles("it")
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class BasicAuthenticationIntegrationTests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void accessWithValidCredentials() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc
.perform(get("/users").with(httpBasic("[email protected]", "password")))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
@Test
public void accessWithInValidCredentials() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc
.perform(get("/users").with(httpBasic("[email protected]", "invalidPassword")))
.andExpect(status().is4xxClientError());
}
}Demo
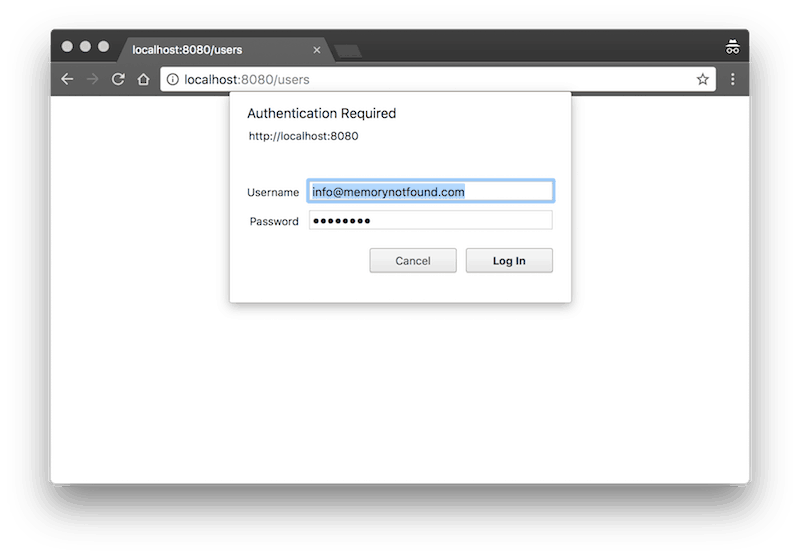
When we access the protected resource, we receive a basic authentication popup.
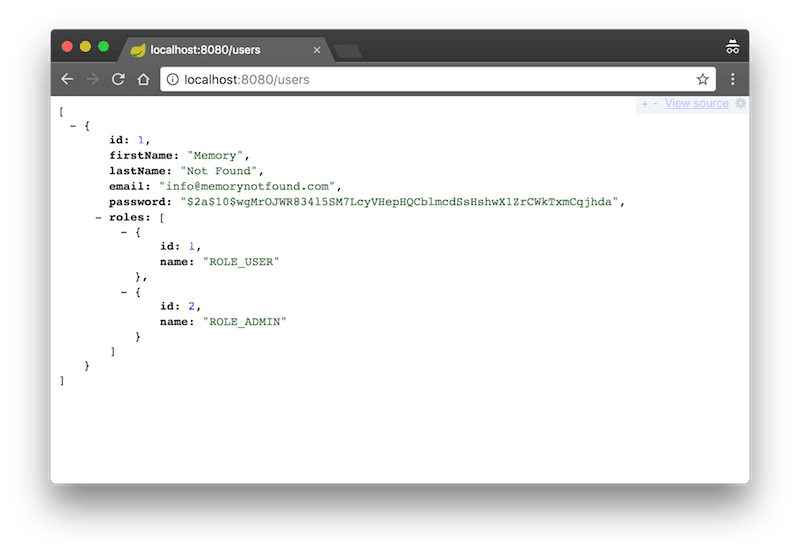
When the user is authenticated, we can see the following result.
References
- Spring Security Documentation
- Hibernate Documentation
- Spring Data JPA Documentation
- BCryptPasswordEncoder JavaDoc
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter JavaDoc
- UserDetailsService JavaDoc


Hi, can you tell me about how add to new User() exist role?
What to do if role exist in DB?
You need to make sure your cascading is handled correctly.
This can be configured using the @ManyToMany annotation using the cascade property.
In your situation you’re probably saving a detached entity.
You can merge your entity by using ‘cascade= {CascadeType.MERGE, CascadeType.PERSIST}’
Hope this helps you,
Cheers
You need to make sure your cascading is handled correctly.
This can be configured using the @ManyToMany annotation using the cascade property.
In your situation you’re probably saving a detached entity.
You can merge your entity by using ‘cascade= {CascadeType.MERGE, CascadeType.PERSIST}’
Hope this helps you,
Cheers
:)