Hibernate/JPA Single Table Inheritance Example
In this tutorial, we show how to map entity hierarchies onto database tables. There are several ways of mapping inheritance to the database. Here, we’ll look into Hibernate/JPA single table inheritance.
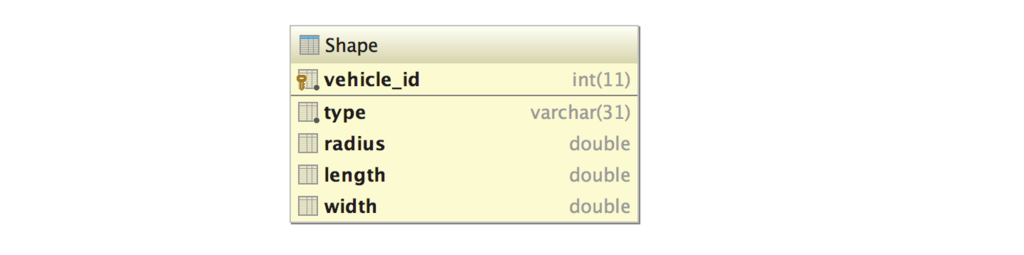
The single table inheritance strategy maps all subclasses to only one database table. Each subclass declares its own persistent properties. Version and id properties are assumed to be inherited from the root class.
When no explicit inheritance strategy is registered, Hibernate/JPA will choose the SINGLE_TABLE inheritance strategy by default.SINGLE_TABLE inheritance performs the best in terms of executed SQL statements. However, you cannot use NOT NULL constraints on the column-level. You can still use triggers and rules to enforce such constraints, but it’s not as straightforward.
Maven Dependencies
We use Apache Maven to manage the projects dependencies.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.memorynotfound.db.hibernate.configuration</groupId>
<artifactId>entity-manager</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>HIBERNATE - ${project.artifactId}</name>
<url>https://memorynotfound.com</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Creating Models + Hibernate/JPA Mappings
Each subclass in a hierarchy must define a unique discriminator value, which is used to differentiate between rows belonging to separate subclass types. If this is not specified, the DTYPE column is used as a discriminator, storing the associated subclass name.
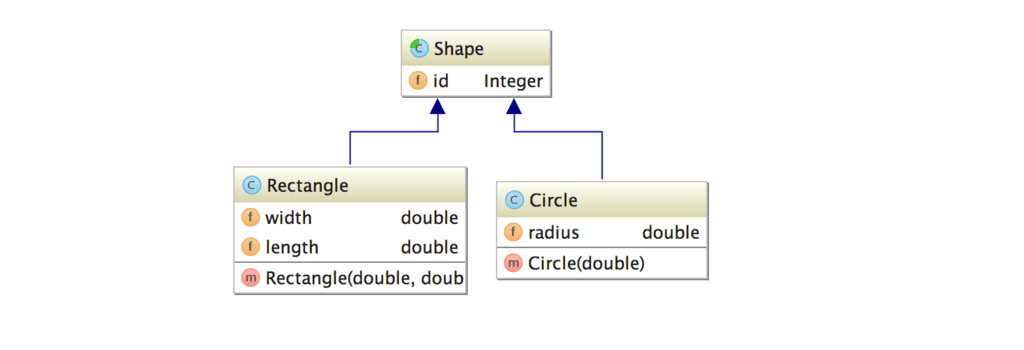
The inheritance strategy is defined on the abstract super class, using the @Inheritance annotation. In this example, we used InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE. This means, all concrete subclasses will be stored in one table. You can optionally specify a discriminator column name. This column is registered by the @DiscriminatorColumn, if omitted the default DTYPE name is used.
package com.memorynotfound.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@DiscriminatorColumn(name = "type")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
public abstract class Shape {
@Id
@Column(name = "vehicle_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
}The first concrete subclass named Circle.java is annotated with the @DiscriminatorValue annotation. Meaning the the discriminator value for this object.
package com.memorynotfound.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue(value = "Circle")
public class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle{" +
"radius=" + radius +
'}';
}
}The second concrete subclass named Rectangle.java is annotated with the @DiscriminatorValue annotation. Meaning the the discriminator value for this object.
package com.memorynotfound.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue(value = "Rectangle")
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double width;
private double length;
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Rectangle{" +
"width=" + width +
", length=" + length +
'}';
}
}If you prefer XML over Annotations, you can use the equivalent JPA XML mapping. This file is located in the src/main/resources/META-INF folder and is named orm.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<entity-mappings xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/orm"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/orm
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/orm_2_0.xsd" version="2.0">
<!-- abstract shape -->
<entity class="com.memorynotfound.hibernate.Shape">
<inheritance strategy="SINGLE_TABLE"/>
<discriminator-column name="type"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<generated-value strategy="IDENTITY"/>
<column name="shape_id"/>
</id>
</attributes>
</entity>
<!-- circle concrete subclass -->
<entity class="com.memorynotfound.hibernate.Circle">
<discriminator-value>circle</discriminator-value>
<attributes>
<basic name="radius"/>
</attributes>
</entity>
<!-- rectangle concrete subclass -->
<entity class="com.memorynotfound.hibernate.Rectangle">
<discriminator-value>rectangle</discriminator-value>
<attributes>
<basic name="length"/>
<basic name="width"/>
</attributes>
</entity>
</entity-mappings>Hibernate/JPA Configuration
We configure the JPA Persistence Unit using the persistence.xml file, which is located in the src/main/resources/META-INF directory.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence version="2.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_1.xsd">
<persistence-unit name="mnf-pu" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<mapping-file>META-INF/orm.xml</mapping-file>
<properties>
<!-- Configuring JDBC properties -->
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/memorynotfound?serverTimezone=Europe/Brussels"/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root"/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value=""/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!-- Hibernate properties -->
<property name="hibernate.dialect" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect"/>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create-drop"/>
<property name="hibernate.format_sql" value="true"/>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>Create, Run and Test application
package com.memorynotfound.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.*;
public class App {
public static void main (String...args) throws InterruptedException {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("mnf-pu");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
em.getTransaction().begin();
Circle circle = new Circle(13.05);
em.persist(circle);
em.getTransaction().commit();
em.getTransaction().begin();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(5.02, 10.45);
em.persist(rectangle);
em.getTransaction().commit();
List accounts = em
.createQuery("select a from Shape a")
.getResultList();
emf.close();
}
} Since we used the SINGLE_TABLE inheritance strategy, a single table is created.
create table Shape (
vehicle_id integer not null auto_increment,
radius double precision,
length double precision,
width double precision,
type varchar(31) not null,
primary key (vehicle_id)
)Here is the SQL INSERT statement.
insert into Shape (radius, type) values (?, 'Circle')
insert into Shape (length, width, type) values (?, ?, 'Rectangle')The SQL SELECT statement of a SINGLE_TABLE inheritance is the fastest, because the select statement is executed for a single table.
select
shape0_.shape_id as shape_id2_0_,
shape0_.radius as radius3_0_,
shape0_.length as length4_0_,
shape0_.width as width5_0_,
shape0_.type as type1_0_
from
Shape shape0_References
- Single Table Inheritance – Hibernate Documentation
- @Inheritance JavaDoc
- @DiscriminatorValue JavaDoc
- InheritanceType JavaDoc



