Spring Boot ActiveMQ Queue Point to Point Configuration Example
In the following tutorial we show how to use spring boot and ActiveMQ to send and receive messages to -and from a queue.
Queue Point to Point Pattern
Message queues provide an asynchronous communications protocol, meaning that the sender and receiver of the message do not need to interact with the message queue at the same time. Messages placed onto the queue are stored until the recipient retrieves them. Message queues have implicit or explicit limits on the size of data that may be transmitted in a single message and the number of messages that may remain outstanding on the queue. The following illustration demonstrates a point-to-point communication between a sender and a receiver.
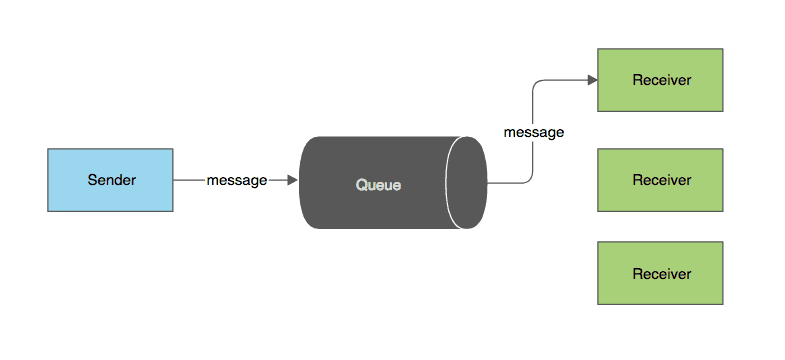
Queue Point to Point Example
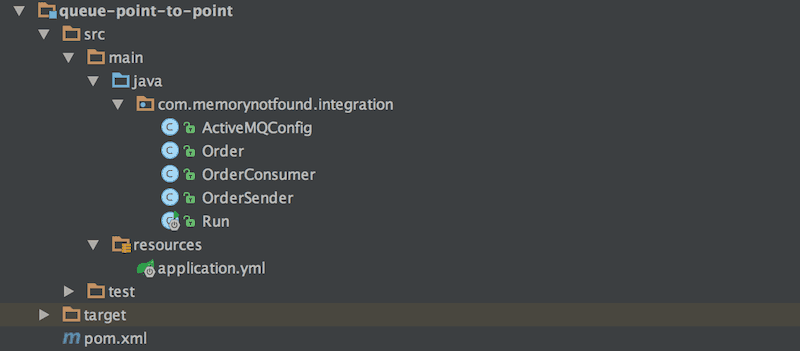
Project Structure
Let’s start by looking at the project structure.
Maven Dependencies
We use Apache Maven to manage our project dependencies. Make sure the following dependencies reside on the class-path. Since we are using LocalDateTime we need to register the com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310 dependency. This’ll automatically convert the specified object into the correct JSON representation.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.memorynotfound.integration.jms.activemq</groupId>
<artifactId>queue-point-to-point</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<url>https://memorynotfound.com</url>
<name>Spring Integration + ActiveMQ - ${project.artifactId}</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.7.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId>
<artifactId>activemq-broker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Order Object
In this example we are sending and receiving objects of type Order to and from a ActiveMQ queue.
package com.memorynotfound.integration;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class Order implements Serializable {
private String from;
private String to;
private BigDecimal amount;
private LocalDateTime timestamp;
public Order() {
}
public Order(String from, String to, BigDecimal amount, LocalDateTime timestamp) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.amount = amount;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
}
public String getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(String to) {
this.to = to;
}
public BigDecimal getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(BigDecimal amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public LocalDateTime getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public void setTimestamp(LocalDateTime timestamp) {
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order{" +
"from='" + from + '\'' +
", to='" + to + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
", timestamp=" + timestamp +
'}';
}
}Spring Boot ActiveMQ Configuration
Spring Boot can automatically configure a ConnectionFactory when it detects that ActiveMQ is available on the class-path. If the broker is present, an embedded broker is started and configured automatically (as long as no broker URL is specified through configuration). For conveniences we created and configured an embedded activeMQ server. The application.yml file is located in the src/main/resources/ folder. This configuration file creates and configures an embedded ActiveMQ broker.
Note: we are creating apoint-to-pointqueue communication between thesenderandreceiver, make sure thespring.jms.pub-sub-domainis set tofalse. This specifies that the default destination is a queue. Another thing to notice is we created concurrent listeners. We configured this concurrent listeners using thespring.jms.concurrencyandspring.jms.max-concurrencyproperties. The first property configures the minimum number of concurrent consumers. The latter configures the maximum number of concurrent consumers. We increased this number so there’ll be multiple receivers, but only one receiver can read one message from the queue.
spring:
# Embedded ActiveMQ Configuration Example
activemq:
broker-url: vm://embedded?broker.persistent=false,useShutdownHook=false
in-memory: true
non-blocking-redelivery: true
packages:
trust-all: false
trusted: com.memorynotfound
pool:
block-if-full: true
block-if-full-timeout: -1
create-connection-on-startup: true
enabled: false
expiry-timeout: 0
idle-timeout: 30000
max-connections: 1
maximum-active-session-per-connection: 500
reconnect-on-exception: true
time-between-expiration-check: -1
use-anonymous-producers: true
# Spring JMS Settings
jms:
listener:
acknowledge-mode: auto
auto-startup: true
concurrency: 5
max-concurrency: 5
pub-sub-domain: true
template:
default-destination:
delivery-mode: non_persistent
priority: 100
qos-enabled: true
receive-timeout: 1000
time-to-live: 36000
# Logging configuration print only current thread and messages for tutorial purposes
logging:
pattern:
console: "[%thread]:%msg%n"
level:
- ".=info"
- "com.memorynotfound=debug"
- "org.springframework=info"Spring ActiveMQ Configuration
The @EnableJms enables JMS listener annotated endpoints that are created under the cover by JmsListenerContainerFactory. The JmsListenerContainerFactory is responsible to create the listener container responsible for a particular endpoint. The @EnableJms annotation also enables detection of JmsListener annotations on any Spring-managed beans in the container. The MappingJackson2MessageConverter uses Jackson to convert messages to and from JSON. Notice: we have created a custom ObjectMapper and registered the module JavaTimeModule. This helps Jackson support the jsr-310 time and date modules from Java 8 e.g.: LocalDateTime.
Java Configuration
package com.memorynotfound.integration;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.EnableJms;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MappingJackson2MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageType;
@EnableJms
@Configuration
public class ActiveMQConfig {
public static final String ORDER_QUEUE = "order-queue";
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter() {
MappingJackson2MessageConverter converter = new MappingJackson2MessageConverter();
converter.setTargetType(MessageType.TEXT);
converter.setTypeIdPropertyName("_type");
converter.setObjectMapper(objectMapper());
return converter;
}
@Bean
public ObjectMapper objectMapper(){
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
return mapper;
}
}Sending Messages to a JMS Queue
Now we have configured the ActiveMQ message broker, we can start sending messages to an ActiveMQ Queue. We use the JmsTemplate to send JMS messages to the queue. We simply need to pass in a destination and message arguments and the JmsTemplate handles the rest.
package com.memorynotfound.integration;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import static com.memorynotfound.integration.ActiveMQConfig.ORDER_QUEUE;
@Service
public class OrderSender {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderSender.class);
@Autowired
private JmsTemplate jmsTemplate;
public void sendQueue(Order order) {
log.info("sending with convertAndSend() to queue <" + order + ">");
jmsTemplate.convertAndSend(ORDER_QUEUE, order);
}
}Receiving messages from a JMS Queue
The @JmsListener annotation marks a method to be the target of a JMS message listener on the specified destination.
package com.memorynotfound.integration;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.JmsListener;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Headers;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.jms.Session;
import static com.memorynotfound.integration.ActiveMQConfig.ORDER_QUEUE;
@Component
public class OrderConsumer {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderConsumer.class);
@JmsListener(destination = ORDER_QUEUE)
public void receiveMessage(@Payload Order order,
@Headers MessageHeaders headers,
Message message,
Session session) {
log.info("received <" + order + ">");
}
}Bootstrap Spring Application
We bootstrap the application using Spring Boot. When the application is initialized, we simply send a couple of messages to a JMS queue and print the output to the console.
package com.memorynotfound.integration;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Run implements ApplicationRunner {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Run.class);
@Autowired
private OrderSender orderSender;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) throws Exception {
log.info("Spring Boot ActiveMQ Queue Point to Point Configuration Example");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
Order order = new Order("me", "you", new BigDecimal(i), LocalDateTime.now());
orderSender.sendQueue(order);
}
log.info("Waiting for all ActiveMQ JMS Messages to be consumed");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.exit(-1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Run.class, args);
}
}Example Output
The previous application prints the following output to the console. In the output we can clearly see that we have deployed multiple consumers (subscribers) which all received multiple messages.
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v1.5.7.RELEASE)
...
[main]:Connector vm://embedded started
[main]:Spring Boot ActiveMQ Queue Point to Point Configuration Example
[main]:sending with convertAndSend() to order-queue <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=0, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.577}>
[main]:sending with convertAndSend() to order-queue <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=1, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.664}>
[main]:sending with convertAndSend() to order-queue <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=2, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.670}>
[main]:sending with convertAndSend() to order-queue <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=3, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.677}>
[main]:sending with convertAndSend() to order-queue <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=4, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.681}>
[main]:Waiting for all ActiveMQ JMS Messages to be consumed
[DefaultMessageListenerContainer-2]:received <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=1, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.664}>
[DefaultMessageListenerContainer-1]:received <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=0, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.577}>
[DefaultMessageListenerContainer-1]:received <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=2, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.670}>
[DefaultMessageListenerContainer-2]:received <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=3, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.677}>
[DefaultMessageListenerContainer-1]:received <Order{from='me', to='you', amount=4, timestamp=2017-10-10T08:26:59.681}>
...References
- ActiveMQ Official Website
- ActiveMQ API JavaDoc
- Spring Boot Common Application Properties
- Spring Boot ActiveMQ Documentation
- JmsTemplate JavaDoc
- @JmsListener JavaDoc



